
For infants and young children, testing involves using sensors (which look like small stickers) or probes to measure hearing. The type of tests given depends on age and symptoms. There are several types of hearing tests. An otolaryngologist (ENT), a doctor specializing in treating diseases and conditions of the ears, nose, and throat.An audiologist, a health care provider who specializes in diagnosing, treating, and managing hearing loss.If there is hearing loss, your child may be tested and treated by one of the following providers: Initial hearing tests are often done during regular checkups.
#Weber test ear tv#

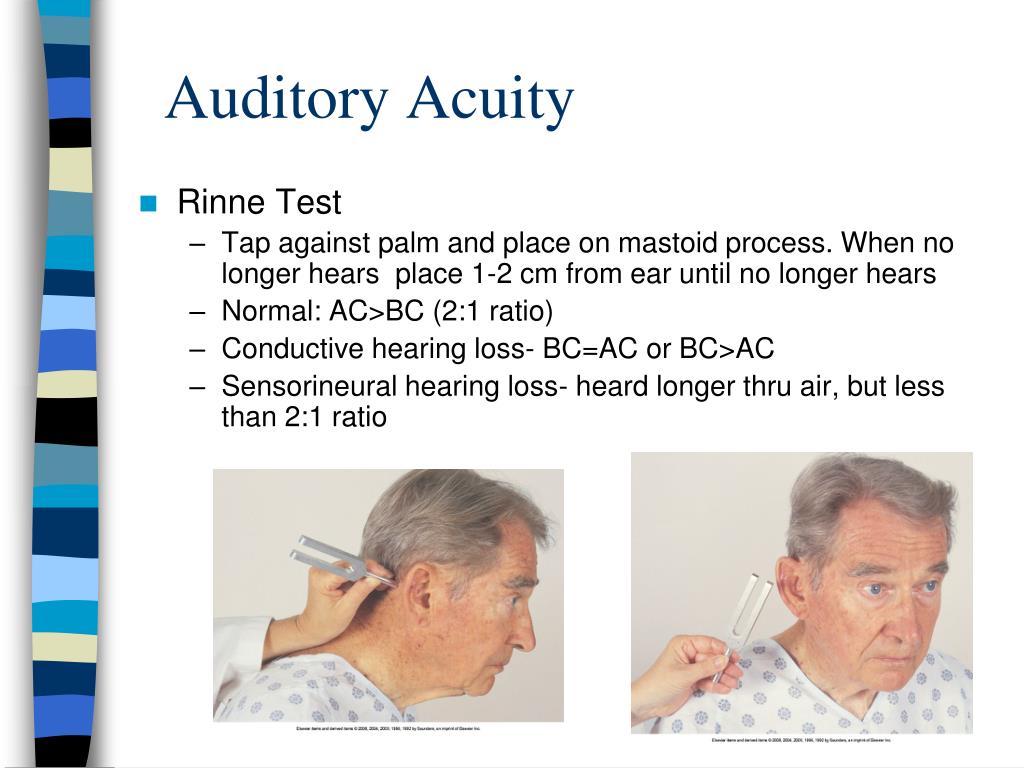
Sensorineural hearing loss is usually permanent. It may be present at birth or show up late in life. This type of hearing loss is caused by a problem with the structure of the ear and/or with the nerves that control hearing. Sensorineurual (also called nerve deafness).Conductive hearing loss is usually mild, temporary, and treatable. It's most common in infants and young children and is often caused by ear infections or fluid in the ears. This type of hearing loss is caused by a blockage of sound transmission into the ear. There are three main types of hearing loss: Hearing loss happens when there is a problem with one or more parts of the ear, the nerves inside the ear, or the part of the brain that controls hearing. This information is translated into the sounds you hear. The vibration moves the waves farther into the ear, where it triggers nerve cells to send sound information to your brain. Normal hearing happens when sound waves travel into your ear, causing your eardrum to vibrate. Even a temporary hearing loss can make it harder for a child to understand spoken language and learn to speak.

That's because normal hearing is essential for language development in babies and toddlers. Although hearing loss can occur at any age, hearing problems in infancy and early childhood can have serious consequences. These tests measure how well your child is able to hear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
